How have fruits contributed to the success of angiosperms? The answer lies in their remarkable adaptations, nutritional value, environmental resilience, and evolutionary significance. From aiding seed dispersal to attracting pollinators, fruits have played a pivotal role in the dominance of angiosperms in the plant kingdom.
The development of fruits revolutionized seed dispersal, allowing angiosperms to expand their range and diversify their habitats. Fleshy fruits, hooks, and wings are just a few examples of specialized adaptations that facilitate the movement of seeds by animals, wind, and water.
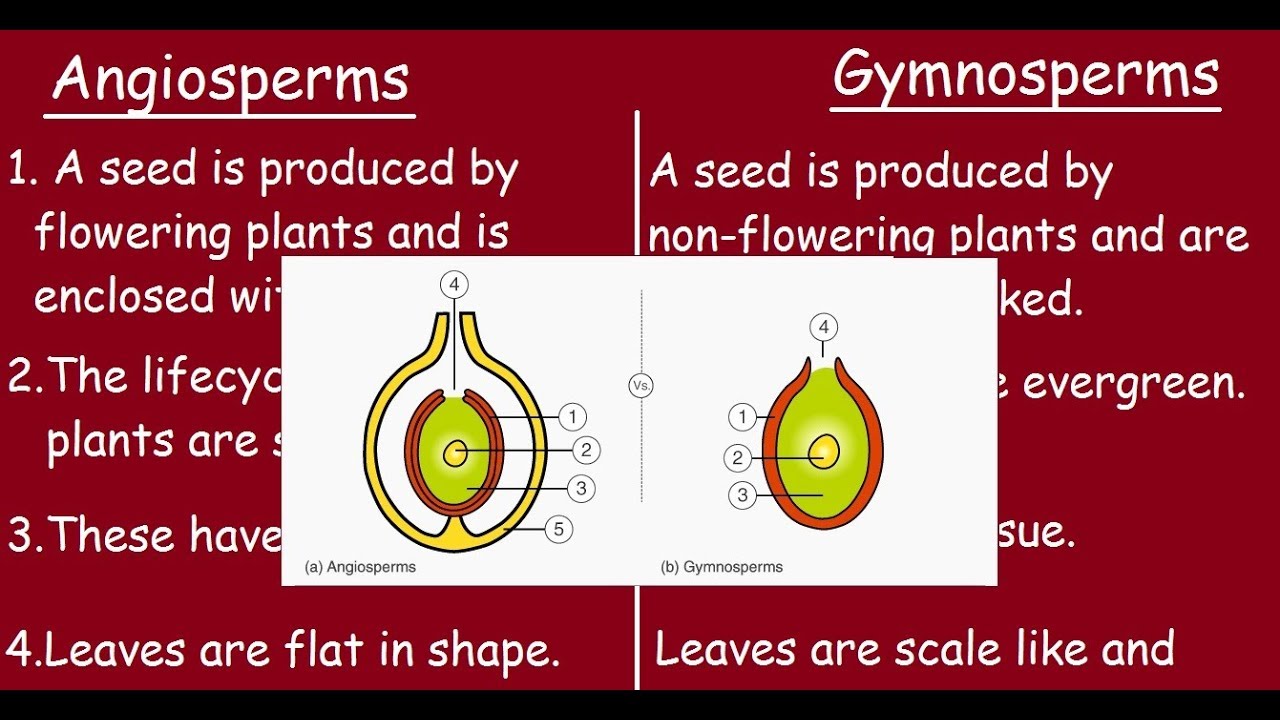
Reproductive Adaptations
The development of fruits revolutionized seed dispersal, expanding the range and diversity of angiosperms. Fleshy fruits, such as berries and drupes, entice animals to consume them, aiding in seed distribution over long distances through their droppings. Other adaptations include hooks and wings that enable fruits to cling to fur or be carried by wind, extending their reach even further.
Role of Animals in Fruit Dispersal
- Animals play a crucial role in fruit dispersal, consuming and transporting seeds to new locations.
- Birds, mammals, and insects contribute to seed dispersal, shaping the distribution patterns of angiosperms.
- The co-evolutionary relationship between fruits and animals has driven the diversification of both groups.
Nutritional Advantages: How Have Fruits Contributed To The Success Of Angiosperms

Fruits provide essential nutrients that support angiosperm growth and survival. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which play vital roles in photosynthesis, metabolism, and defense against pathogens.
Essential Nutrients in Fruits
- Vitamins A, C, and E are essential for photosynthesis and plant growth.
- Minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium contribute to cell structure and enzyme function.
- Antioxidants protect plants from oxidative damage caused by environmental stresses.
Attracting Pollinators and Beneficial Organisms, How have fruits contributed to the success of angiosperms
Fruits also play a role in attracting pollinators and other beneficial organisms. The sweet taste and vibrant colors of fruits attract insects and animals that aid in pollination and seed dispersal.
Environmental Resilience
Fruits contribute to the adaptability and resilience of angiosperms in various environmental conditions. Some fruits offer protection from drought, extreme temperatures, and herbivores, ensuring seed survival and plant establishment.
Fruits for Environmental Resilience
- Thick-skinned fruits, such as nuts and acorns, provide protection from drought and extreme temperatures.
- Fruits with spines or thorns deter herbivores, reducing seed predation.
- Fruits that produce toxins can repel animals and protect seeds from damage.
Role in Soil Conservation and Nutrient Cycling
Fruits also contribute to soil conservation and nutrient cycling. They provide organic matter that enriches the soil, enhancing its fertility and water retention capacity.
Fruits have played a pivotal role in the evolutionary success of angiosperms, as they have evolved to attract animals for seed dispersal, thereby ensuring the survival of the species. Similarly, in the context of bankruptcy, Chapter 7 bankruptcy has a success rate of around 35%, indicating that a significant proportion of individuals are able to achieve financial recovery through this legal process.
The contribution of fruits to the success of angiosperms highlights the importance of adaptations that promote survival and reproduction, just as the success rate of Chapter 7 bankruptcy demonstrates the potential for individuals to overcome financial adversity and rebuild their lives.
Evolutionary Significance
| Evolutionary Milestone | Key Innovations | Impact on Angiosperms |
|---|---|---|
| Transition from Gymnosperms to Angiosperms | Enclosed seeds within ovaries | Increased seed protection and dispersal efficiency |
| Development of Fleshy Fruits | Enticing to animals for seed dispersal | Expanded angiosperm range and diversity |
| Co-evolution with Animals | Mutualistic relationships for seed dispersal | Diversification of both fruits and animals |
Conclusion

The co-evolution of fruits and animals has further shaped the diversity of both groups. Fruits provide essential nutrients for animals, while animals aid in seed dispersal, creating a mutually beneficial relationship that has driven the success of angiosperms. Today, fruits continue to play a crucial role in plant ecology, contributing to nutrient cycling, soil conservation, and the survival of countless species.

