Consumer finance companies play a crucial role in the financial landscape, providing a wide range of products and services to individuals and families. From personal loans to mortgages and credit cards, these companies offer solutions to meet diverse financial needs.
The consumer finance industry is vast and complex, with various types of companies offering unique products and services. Banks, credit unions, and non-bank lenders are just a few examples of the players in this dynamic market.
Consumer Finance Industry Overview
The consumer finance industry plays a pivotal role in the global economy by providing access to credit and financial services for individuals and households. It encompasses a wide range of institutions, including banks, credit unions, and non-bank lenders, that offer various products and services such as personal loans, mortgages, credit cards, and more.
According to a report by Research and Markets, the global consumer finance market was valued at $17.6 trillion in 2021 and is projected to reach $25.4 trillion by 2027, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% during the forecast period.
Key trends shaping the industry include the rise of digital lending, the growing demand for financial inclusion, and the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in credit risk assessment.
Finance internships offer valuable opportunities for students to gain practical experience in the industry. For those seeking a summer internship in 2023, numerous options are available. Visit finance internships summer 2023 for a comprehensive list of programs, including internships at leading investment banks, asset management firms, and corporations.
Types of Consumer Finance Companies
There are several types of consumer finance companies, each with unique characteristics, products, and services:
- Banks:Traditional financial institutions that offer a wide range of consumer finance products, including personal loans, mortgages, and credit cards. They typically have a large customer base and a well-established branch network.
- Credit Unions:Not-for-profit financial cooperatives owned by their members. They offer similar products and services as banks but often have lower interest rates and fees.
- Non-Bank Lenders:Financial institutions that do not accept deposits but specialize in providing consumer loans. They may offer higher interest rates than banks and credit unions but can be more flexible in their lending criteria.
Consumer Lending Products and Services
Consumer finance companies offer a variety of lending products and services to meet the diverse needs of individuals and households:
- Personal Loans:Unsecured loans used for various purposes, such as debt consolidation, home improvement, and medical expenses.
- Mortgages:Secured loans used to purchase or refinance real estate.
- Credit Cards:Revolving lines of credit that allow consumers to make purchases and pay them off over time.
The approval of a loan application, interest rates, and repayment terms are influenced by factors such as the borrower’s credit score, income, debt-to-income ratio, and the purpose of the loan.
Consumer Finance Regulations
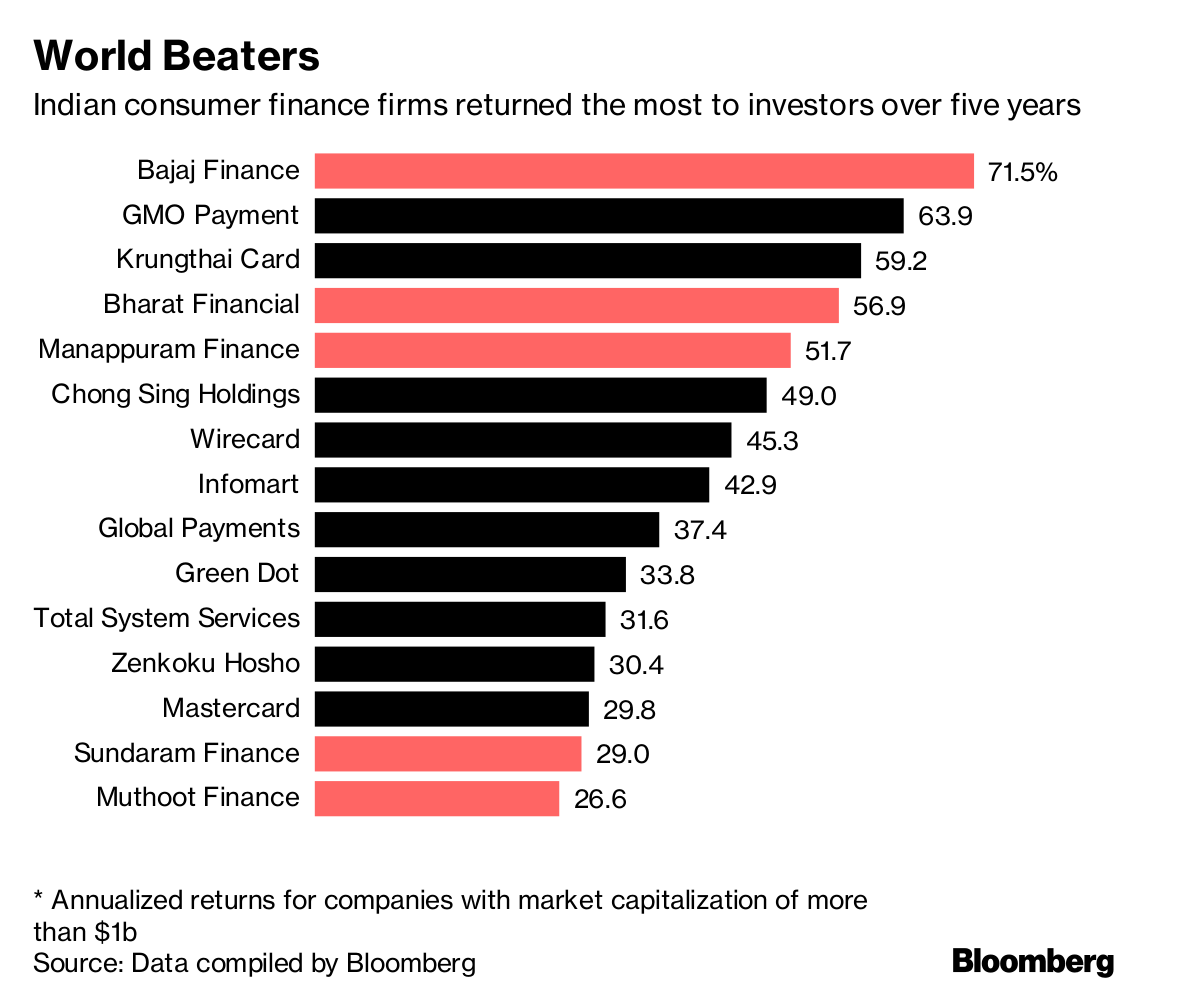
Consumer finance companies are subject to a comprehensive regulatory framework designed to protect consumers and ensure the stability of the financial system:
- Truth in Lending Act (TILA):Requires lenders to provide clear and concise information about the terms and conditions of loans, including the interest rate, fees, and repayment schedule.
- Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act:Aimed at preventing another financial crisis, it includes provisions to protect consumers from predatory lending practices, such as the ability to repay rule.
Compliance with these regulations ensures that consumers are treated fairly and have access to transparent and affordable credit.
Credit Scoring and Risk Management
Credit scoring is a statistical tool used to assess the creditworthiness of a borrower and predict the likelihood of default.
- Credit Scores:Calculated based on factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, and new credit inquiries.
- Credit Bureaus:Companies that collect and maintain credit information on individuals and businesses.
Lenders use credit scores to determine loan eligibility, interest rates, and repayment terms. A higher credit score indicates a lower risk of default and can lead to more favorable loan terms.
Consumer Financial Education and Protection: Consumer Finance Companies
Consumer finance companies have a responsibility to promote financial literacy and protect consumers from predatory lending practices:
- Financial Education:Offering resources and programs to help consumers understand credit, budgeting, and other financial management skills.
- Consumer Protection:Enforcing regulations and working with consumer protection agencies to prevent unfair and deceptive lending practices.
These efforts help consumers make informed financial decisions and avoid falling victim to financial scams.
As the summer of 2023 approaches, ambitious students eager to gain hands-on experience in the financial industry are actively seeking finance internships . These internships provide invaluable opportunities for aspiring professionals to learn the intricacies of the financial world, network with industry leaders, and gain practical skills that will enhance their future careers.
Technology and Innovation in Consumer Finance
Technology is transforming the consumer finance industry:
- Digital Lending:Online and mobile platforms that streamline the loan application and approval process.
- Mobile Banking:Allows consumers to manage their finances and make payments from their mobile devices.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):Used for credit risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized financial advice.
These innovations are improving access to credit, enhancing convenience, and reducing costs for both consumers and lenders.
Case Studies and Examples
Example 1: Affirm, a leading digital lending platform, has revolutionized consumer financing by offering point-of-sale loans for online and offline purchases. Their AI-powered risk assessment model enables faster and more inclusive lending decisions.
Example 2: Greenlight, a financial technology company, provides debit cards and a mobile banking app designed for children and teens. Their mission is to promote financial literacy and empower young people to make responsible financial decisions.
Final Review
As the consumer finance industry continues to evolve, technology and innovation are transforming the way companies operate. Digital lending, mobile banking, and artificial intelligence are shaping the future of the industry, providing consumers with greater convenience and access to financial services.
Consumer finance companies have a responsibility to promote financial literacy and protect consumers from predatory lending practices. By providing financial education initiatives and implementing consumer protection measures, these companies can empower individuals to make informed financial decisions and achieve their financial goals.


