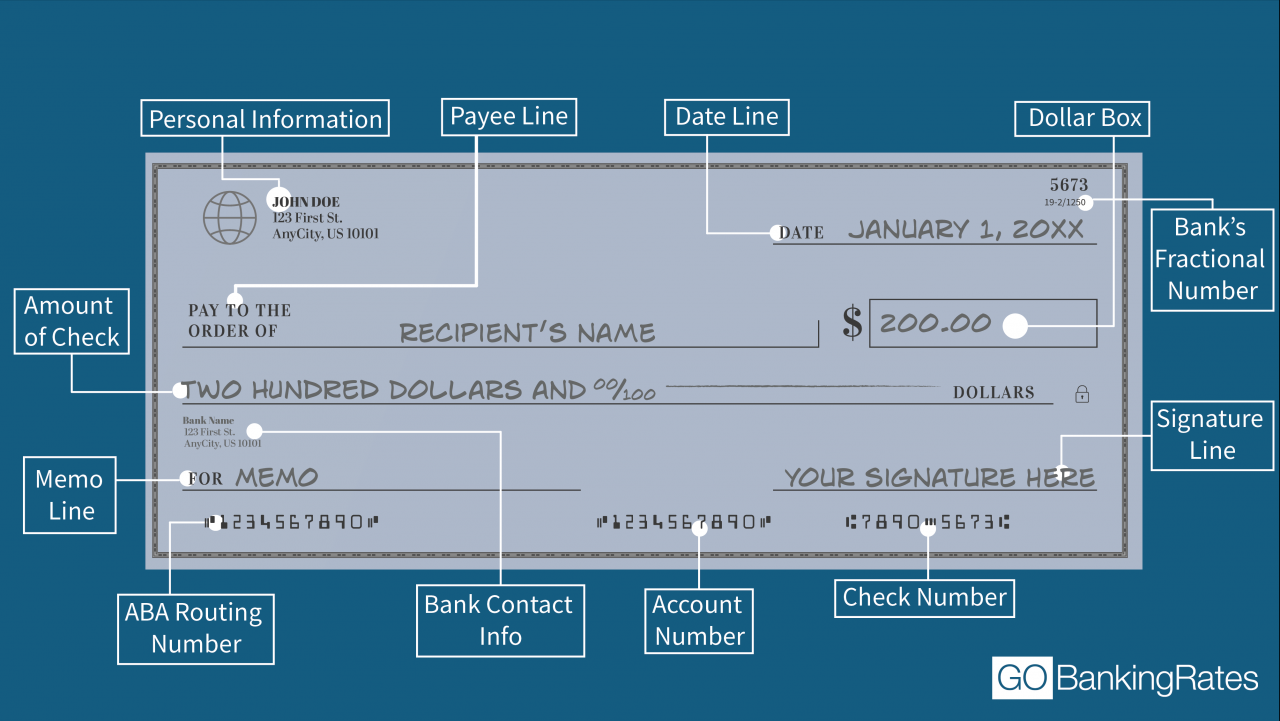
Deep brain stimulation for parkinson’s disease success rate – Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has emerged as a promising treatment for Parkinson’s disease, offering significant symptom relief and improved quality of life for many patients. This article delves into the success rates, benefits, and considerations associated with DBS for Parkinson’s disease.
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement, balance, and coordination. Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowed movement), and postural instability. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that has been shown to be effective in improving motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Deep brain stimulation has emerged as a promising treatment for Parkinson’s disease, with success rates varying depending on individual circumstances. If you’re looking to manage succession matters in Louisiana without legal assistance, this guide provides valuable insights. Notably, deep brain stimulation has shown promising outcomes in alleviating symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, offering hope to those affected by this condition.
DBS for Parkinson’s Disease
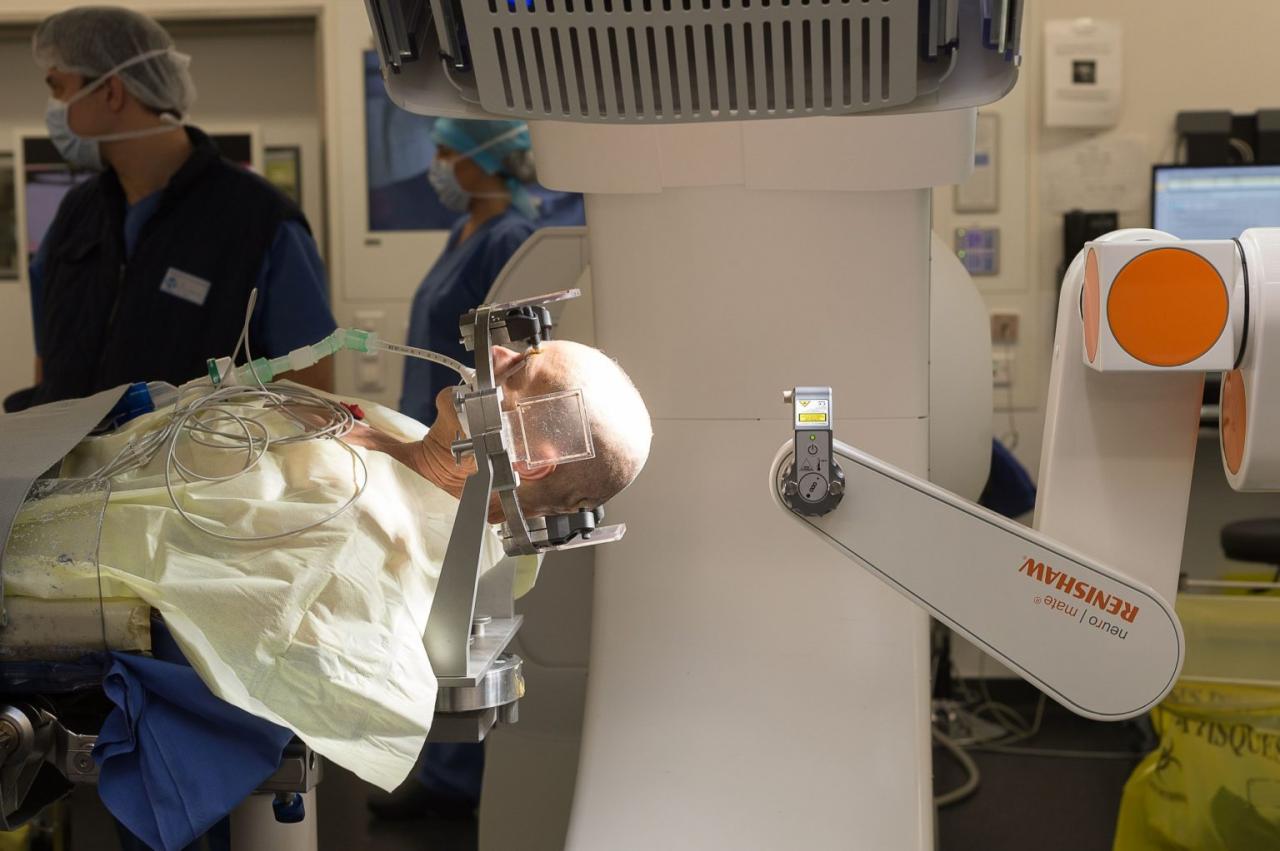
DBS involves implanting electrodes into specific areas of the brain that are responsible for controlling movement. The electrodes are connected to a pacemaker-like device that sends electrical impulses to the brain. These impulses help to regulate brain activity and improve motor function.
Surgical Procedure for DBS, Deep brain stimulation for parkinson’s disease success rate
DBS surgery is typically performed in two stages. In the first stage, the electrodes are implanted into the brain. In the second stage, the pacemaker-like device is implanted under the skin of the chest or abdomen.
Success Rate of DBS
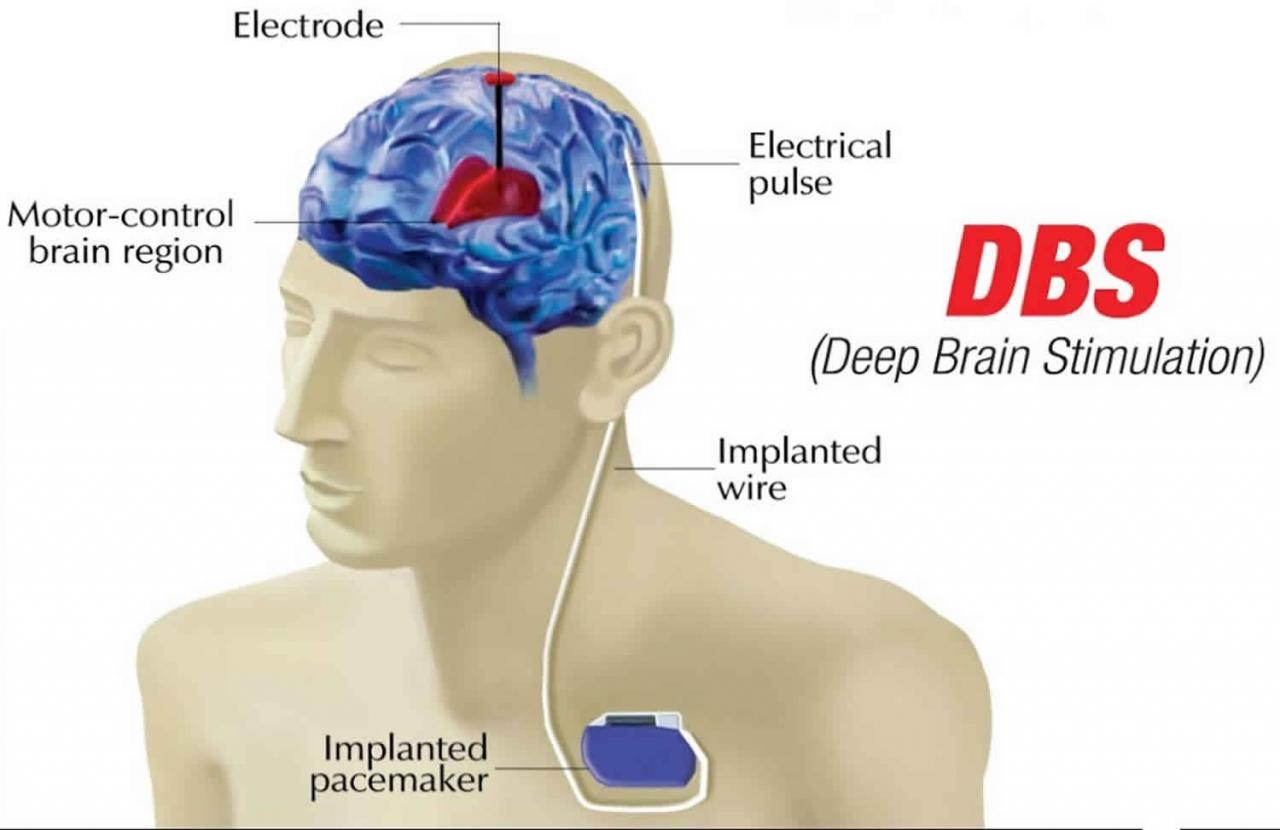
DBS has been shown to be effective in improving motor symptoms in up to 80% of patients with Parkinson’s disease. The success rate of DBS is influenced by a number of factors, including the patient’s age, the severity of their symptoms, and the location of the electrodes.
Benefits of DBS: Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson’s Disease Success Rate
DBS can provide a number of benefits for patients with Parkinson’s disease, including:
- Improved motor symptoms, such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia
- Reduced need for medication
- Improved quality of life
Risks and Complications of DBS
DBS is a relatively safe procedure, but there are some potential risks and complications associated with the surgery and the use of the device. These risks include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Stroke
- Hardware failure
The risks of DBS can be minimized by carefully selecting patients for surgery and by using experienced surgeons and medical staff.
Patient Selection and Evaluation
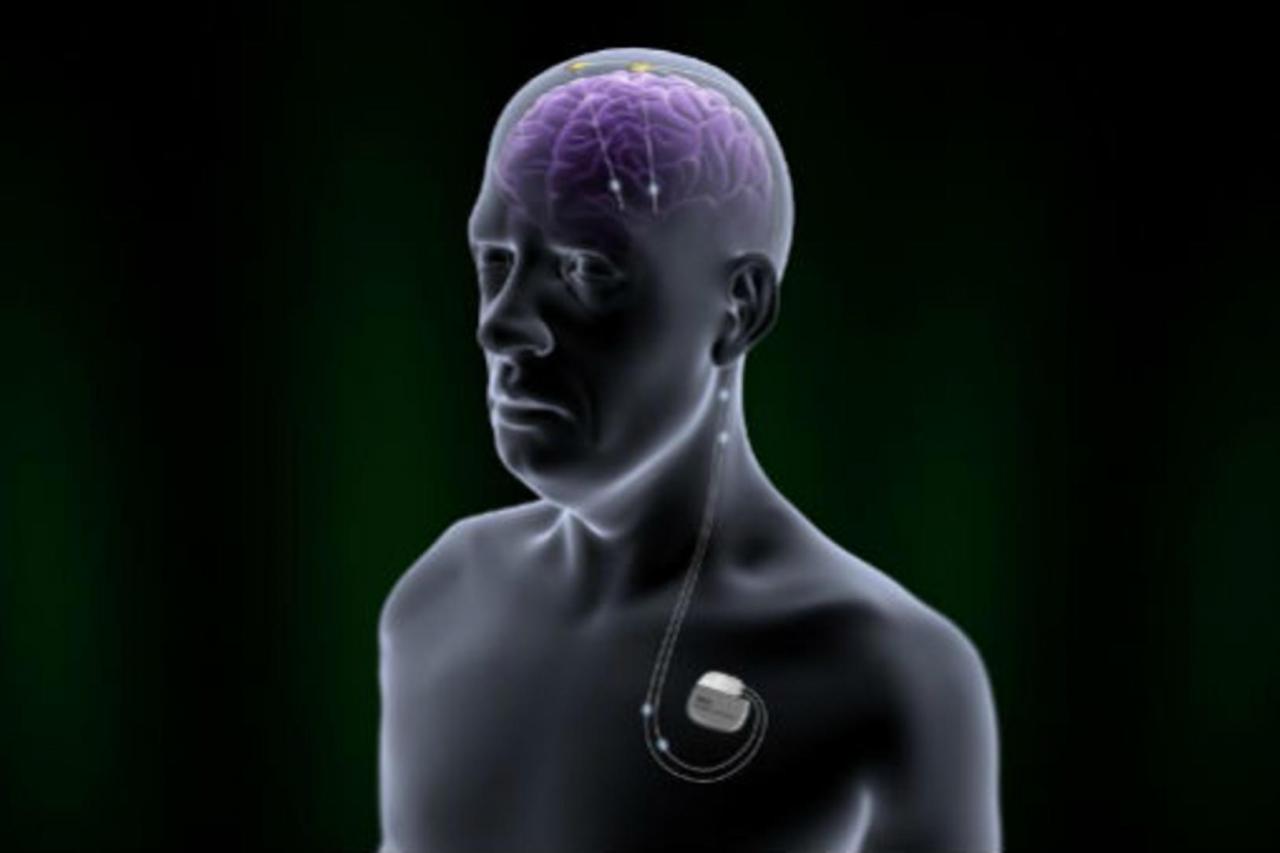
Patients who are considering DBS for Parkinson’s disease should undergo a thorough evaluation to determine if they are a good candidate for the procedure. The evaluation typically includes a physical examination, a neurological examination, and a review of the patient’s medical history.
Long-Term Outcomes of DBS
DBS has been shown to be effective in improving motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease for up to 10 years. However, the long-term efficacy of DBS may vary depending on the individual patient.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, DBS has proven to be a highly effective treatment for Parkinson’s disease, significantly reducing symptoms and enhancing patients’ well-being. While the success rate and long-term outcomes may vary, DBS offers a valuable therapeutic option for carefully selected patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease.