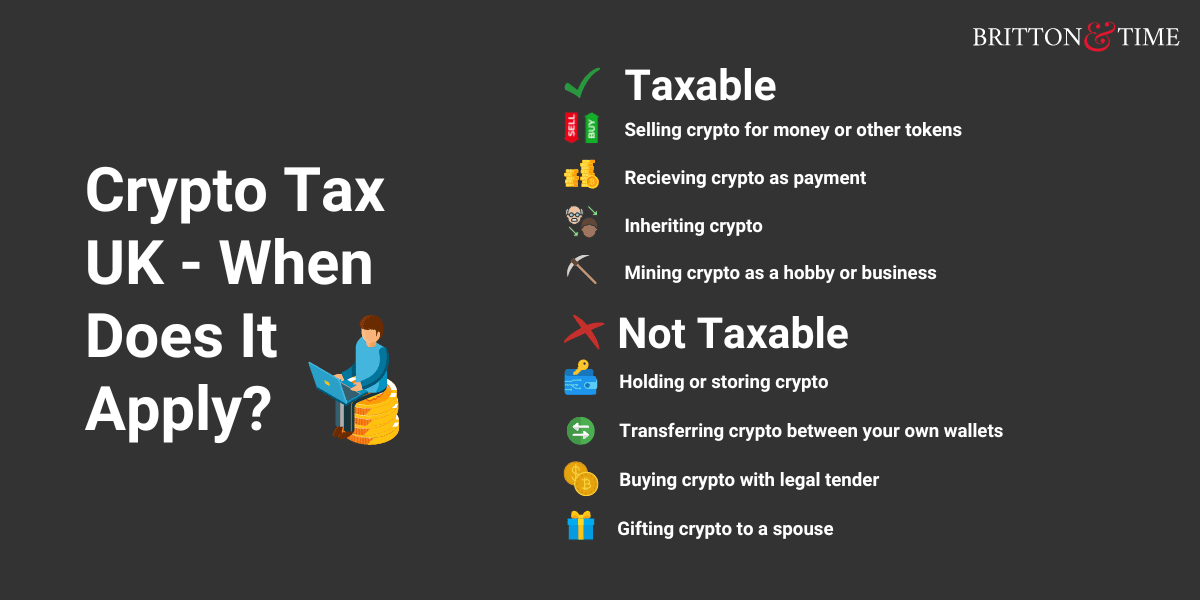
With the rise of cryptocurrency, the question of taxation has become increasingly important. Do you have to pay taxes on crypto? The answer is not always straightforward and can vary depending on several factors, including the type of transaction, your jurisdiction, and your individual circumstances.
This comprehensive guide will explore the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation, providing you with the knowledge you need to navigate this evolving landscape.
In a daring cyber heist, teenage gamers swiped $24 million in cryptocurrency from a prominent online game. The teens allegedly used sophisticated hacking techniques to gain access to player accounts and pilfer their digital assets, including Bitcoin and Ethereum. Authorities are investigating the incident and seeking to apprehend the perpetrators.
As the world of cryptocurrency continues to evolve, so too do the tax implications surrounding it. Understanding how to properly report and pay taxes on your crypto activities is crucial to avoid any potential legal or financial penalties.
Cryptocurrency Taxation Fundamentals: Do You Have To Pay Taxes On Crypto

The taxation of cryptocurrency is a complex and evolving area. In general, cryptocurrency is treated as property for tax purposes, meaning that it is subject to capital gains and losses when sold or traded. The tax treatment of crypto can vary depending on the jurisdiction, so it is important to consult with a tax professional to determine the specific rules that apply in your case.
Types of Cryptocurrency Transactions Subject to Taxation
- Buying and selling cryptocurrency
- Trading cryptocurrency on exchanges
- Mining cryptocurrency
- Staking and lending cryptocurrency
- Receiving cryptocurrency as payment for goods or services
Taxation of Crypto Mining
Mining cryptocurrency is the process of verifying and adding new transactions to the blockchain. Miners are rewarded for their work with cryptocurrency. The tax treatment of crypto mining depends on the jurisdiction, but it is generally considered to be business income.
This means that miners are subject to income tax on the value of the cryptocurrency they mine, and they can also deduct expenses related to mining, such as the cost of electricity and equipment.
In a shocking incident, teenage gamers have allegedly stolen a staggering $24 million worth of cryptocurrency from a popular online game. According to reports, the teens used a sophisticated hacking technique to access and siphon off the funds, leaving the game’s developers and players reeling in disbelief.
Details of the heist are still emerging, but it has sent shockwaves through the gaming community, raising concerns about the security of online gaming platforms.
Cryptocurrency Staking and Lending
Staking and lending cryptocurrency are two ways to earn passive income from your crypto holdings. Staking involves holding a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet to support the network. Lenders lend their cryptocurrency to borrowers in exchange for interest.
Both staking and lending can generate taxable income, which is typically taxed as ordinary income.
Cryptocurrency Trading and Investment, Do you have to pay taxes on crypto
Buying, selling, and trading cryptocurrency can be a taxable event. Short-term capital gains are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, while long-term capital gains are taxed at a lower rate. The holding period for cryptocurrency is generally one year, so any crypto that you sell or trade within one year of acquiring it will be taxed as a short-term capital gain.
Ending Remarks

Navigating the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation can be a daunting task, but it is essential to ensure compliance with the law and avoid any potential penalties. By understanding the tax implications of different types of crypto transactions, you can make informed decisions about your investments and minimize your tax liability.
Remember to stay up-to-date with the latest tax laws and regulations, as they are subject to change over time.