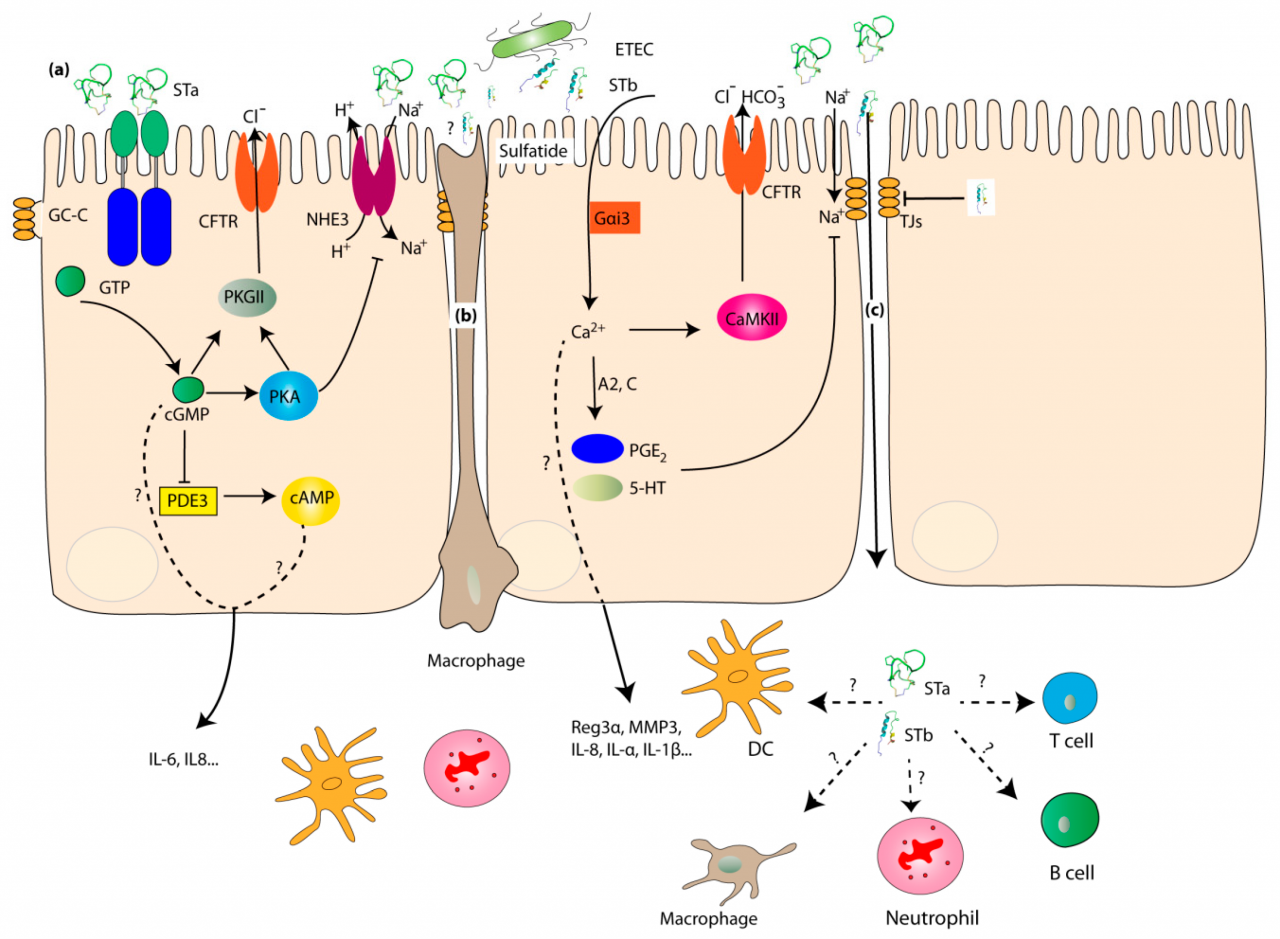
Enterotoxigenic e coli – Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), a prevalent bacterial pathogen, poses a significant global health threat, particularly in developing countries. ETEC infections cause severe diarrhea, leading to dehydration, malnutrition, and even death, primarily affecting children under five years of age.
Tragically, a Lake Orion student has passed away in Houston while attending a robotics competition. The student was a member of the Lake Orion High School Robotics Team and was in Houston for the FIRST Championship. The circumstances surrounding the student’s death are still under investigation.
Our thoughts and condolences go out to the student’s family, friends, and the entire Lake Orion community. Read more
ETEC’s virulence stems from its ability to adhere to and colonize the small intestine, producing potent enterotoxins that disrupt fluid and electrolyte balance, resulting in profuse watery diarrhea. Transmission occurs through contaminated food and water, highlighting the importance of sanitation and hygiene practices.
A Lake Orion High School student has died after collapsing during a robotics competition in Houston, Texas. The student, identified as 17-year-old Ethan Lucero, was competing in the FIRST Tech Challenge World Championship when he suffered a medical emergency. According to a statement from the Lake Orion Community Schools district, Lucero was rushed to a local hospital where he was pronounced dead.
The cause of his death is still under investigation. Read more about the tragic incident here.
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC): Enterotoxigenic E Coli
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) merupakan bakteri patogen yang menjadi penyebab utama diare di seluruh dunia, terutama di negara-negara berkembang. ETEC menghasilkan enterotoksin yang menyebabkan akumulasi cairan di usus halus, yang berujung pada diare berair yang parah.
Patogenesis dan Faktor Virulensi
ETEC berkoloni di usus halus dengan bantuan fimbriae atau faktor kolonisasi. Setelah menempel, bakteri ini melepaskan enterotoksin, seperti heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) dan heat-labile enterotoxin (LT), yang mengaktifkan reseptor spesifik pada sel epitel usus, sehingga menyebabkan peningkatan sekresi klorida dan penghambatan penyerapan natrium, yang menyebabkan diare berair.
Epidemiologi dan Penularan
ETEC tersebar luas di seluruh dunia, dengan prevalensi tertinggi di negara-negara berkembang. Bakteri ini ditularkan melalui konsumsi makanan atau air yang terkontaminasi. Faktor risiko infeksi ETEC meliputi:
- Sanitasi dan kebersihan yang buruk
- Perjalanan ke daerah endemik
- Konsumsi makanan dan minuman yang tidak dimasak dengan benar
Manifestasi Klinis dan Diagnosis
Infeksi ETEC biasanya menyebabkan diare berair yang parah, yang dapat berlangsung selama beberapa hari. Gejala lain mungkin termasuk:
- Mual dan muntah
- Demam
- Kram perut
Diagnosis ETEC dapat ditegakkan melalui pemeriksaan tinja, yang mendeteksi adanya bakteri atau toksinnya.
Pengobatan dan Pencegahan
Pengobatan infeksi ETEC difokuskan pada rehidrasi dan penggantian elektrolit yang hilang akibat diare. Antibiotik mungkin diperlukan dalam beberapa kasus. Tindakan pencegahan untuk mengurangi risiko infeksi ETEC meliputi:
- Mencuci tangan secara teratur
- Memasak makanan dengan benar
- Mengolah air dengan benar
- Mendapatkan vaksinasi (jika tersedia)
Final Review
ETEC infections have far-reaching public health implications, imposing substantial economic burdens and disproportionately impacting vulnerable populations. Surveillance, outbreak investigation, and control measures are crucial for preventing and mitigating ETEC’s impact. Ongoing research and vaccination development efforts aim to reduce the global burden of ETEC infections.