What is the difference between sadness and depression? Sadness is a normal emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. It’s usually caused by a specific event, such as losing a loved one, failing a test, or getting into an argument.
Sadness typically lasts for a short period of time and doesn’t interfere with your ability to function normally. Depression, on the other hand, is a mental illness that can cause persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness. It can interfere with your ability to work, study, sleep, eat, and enjoy life.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to depression, including genetics, brain chemistry, and life experiences. Depression is often treated with medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both.
Definition and Symptoms

Sadness and depression are two distinct emotional states that can be difficult to differentiate. Sadness is a normal human emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. It is typically caused by a specific event or situation, such as losing a loved one, failing a test, or getting into an argument.
Sadness usually lasts for a short period of time and does not interfere with daily life.
Depression, on the other hand, is a mental health disorder that can cause persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness. It is not caused by a specific event or situation, and it can last for weeks, months, or even years. Depression can interfere with all aspects of daily life, including work, school, relationships, and sleep.
Symptoms of Sadness
- Feeling down or blue
- Crying
- Loss of interest in activities
- Difficulty concentrating
- Changes in appetite or sleep
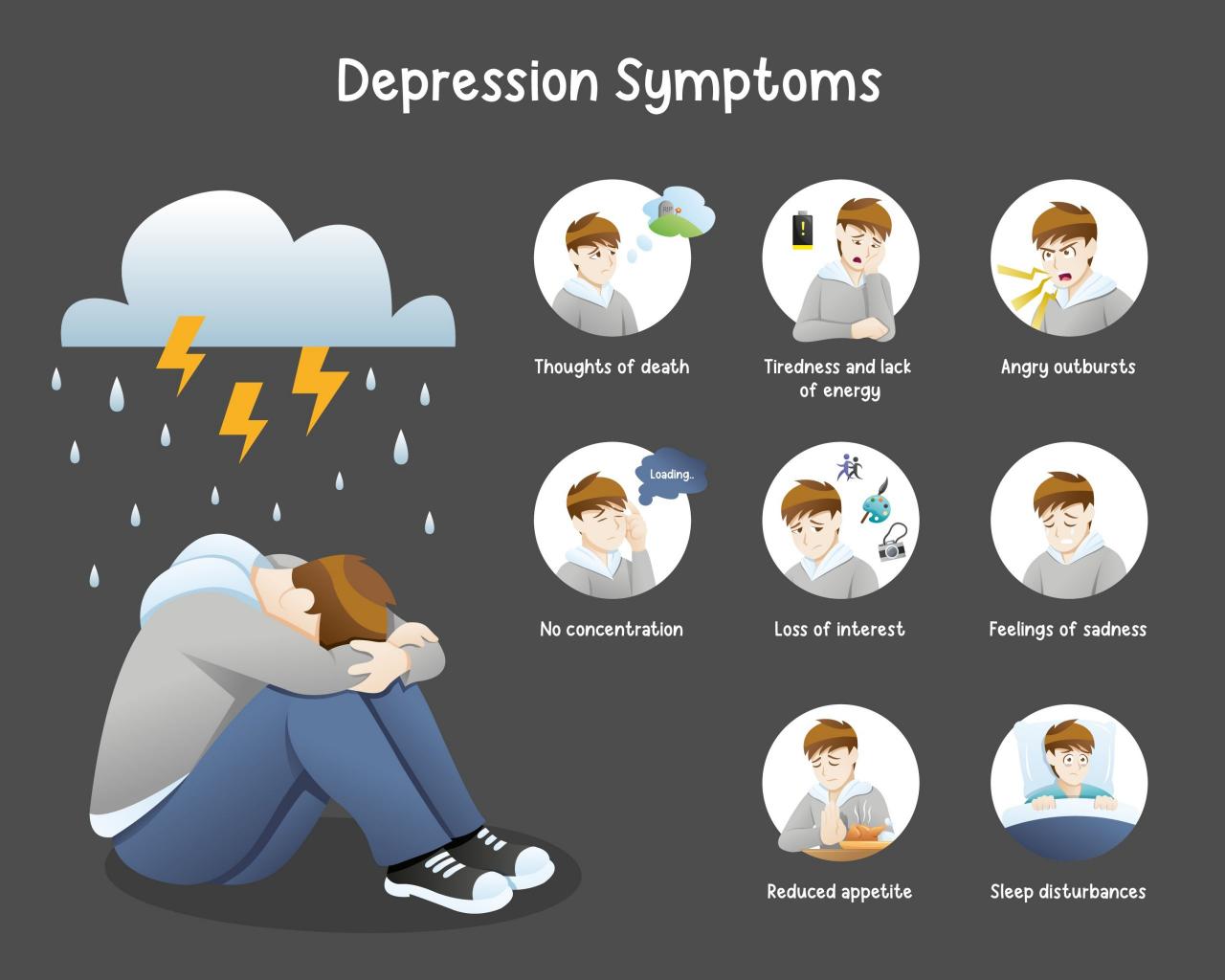
Symptoms of Depression
- Persistent feelings of sadness, emptiness, or hopelessness
- Loss of interest in activities that used to be enjoyable
- Changes in appetite or sleep
- Difficulty concentrating
- Fatigue or loss of energy
- Feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- Thoughts of death or suicide
Causes
Sadness and depression share some common causes, but they differ in their severity and duration. Let’s explore the potential causes of each:
Sadness
Sadness is a temporary emotional state often triggered by specific events or circumstances, such as:
- Personal loss (e.g., death of a loved one, divorce)
- Disappointment (e.g., failing an exam, losing a job)
- Stress (e.g., financial worries, relationship issues)
- Loneliness or isolation
Depression
Depression is a more severe and persistent mental health condition that can have biological, genetic, and environmental causes:
- Biological factors:Imbalances in neurotransmitters (chemical messengers in the brain), hormonal changes, and genetic predispositions can contribute to depression.
- Genetics:Research suggests that depression can run in families, indicating a potential genetic component.
- Environmental influences:Traumatic events, chronic stress, and negative life experiences can increase the risk of developing depression.
Duration and Intensity
Sadness and depression differ significantly in their duration and intensity.
Sadness is typically a temporary emotion that lasts for a few hours, days, or weeks. It is usually triggered by a specific event or situation, such as a loss, disappointment, or failure. The intensity of sadness can vary from mild to moderate, but it usually does not interfere with daily functioning.
Chronic Condition
In contrast, depression is a chronic condition that can last for months or even years. It is not simply a reaction to a specific event or situation, but rather a persistent state of low mood and loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable.
The intensity of depression can range from mild to severe, and it can significantly impair daily functioning.
Impact on Daily Life
Sadness and depression both affect individuals’ daily lives, but the severity and scope of their impact differ. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Sadness typically manifests as a temporary emotional state that may hinder daily activities to some extent. Depression, on the other hand, is a persistent mental health condition that significantly impairs an individual’s functioning in various aspects of life.
Impact on Work and Relationships
Sadness may lead to decreased productivity and focus at work, as well as strained relationships due to irritability or withdrawal. Depression, however, can severely compromise an individual’s ability to perform job duties and maintain healthy relationships, leading to job loss and social isolation.
Impact on Sleep and Physical Health
Sadness can disrupt sleep patterns, causing insomnia or hypersomnia. Depression, on the other hand, often results in chronic sleep disturbances, which can exacerbate physical health conditions such as heart disease, obesity, and diabetes.
Impact on Overall Well-being
Sadness generally does not impair an individual’s overall well-being. However, depression significantly diminishes an individual’s quality of life, causing feelings of hopelessness, worthlessness, and loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable.
Treatment Options
When it comes to addressing sadness and depression, various treatment options are available, ranging from self-care strategies to professional interventions.
Self-Care for Sadness, What is the difference between sadness and depression
For mild sadness, self-care measures can be effective. These may include engaging in activities that bring joy, connecting with loved ones, getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy diet. Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can also be beneficial in managing sadness.
Treatment Options for Depression
Depression requires a more comprehensive approach to treatment, often involving a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a widely used treatment for depression. It involves working with a licensed mental health professional to explore the underlying causes of depression, develop coping mechanisms, and improve overall well-being. Common types of psychotherapy for depression include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and psychodynamic therapy.
Medication
Antidepressants are a class of medications commonly prescribed to treat depression. They work by altering the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which are involved in mood regulation. Different types of antidepressants include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing depression. These may include getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding alcohol and drug use. Engaging in social activities, volunteering, or pursuing hobbies can also provide a sense of purpose and reduce feelings of isolation associated with depression.
Last Recap
Sadness and depression are two very different experiences. Sadness is a normal emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. Depression is a mental illness that can have a significant impact on your life. If you think you may be depressed, it’s important to seek professional help.
Top FAQs: What Is The Difference Between Sadness And Depression
What are the symptoms of depression?
The symptoms of depression can vary from person to person, but some common symptoms include:
- Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness
- Loss of interest in activities that you used to enjoy
- Changes in appetite or sleep patterns
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Fatigue or loss of energy
- Thoughts of self-harm or suicide
What are the causes of depression?
The causes of depression are complex and not fully understood. However, some factors that can contribute to depression include:
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Life experiences, such as trauma, loss, or abuse
How is depression treated?
Depression is often treated with medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both. Medication can help to relieve symptoms of depression, while psychotherapy can help you to learn how to cope with the challenges of depression and develop healthier coping mechanisms.