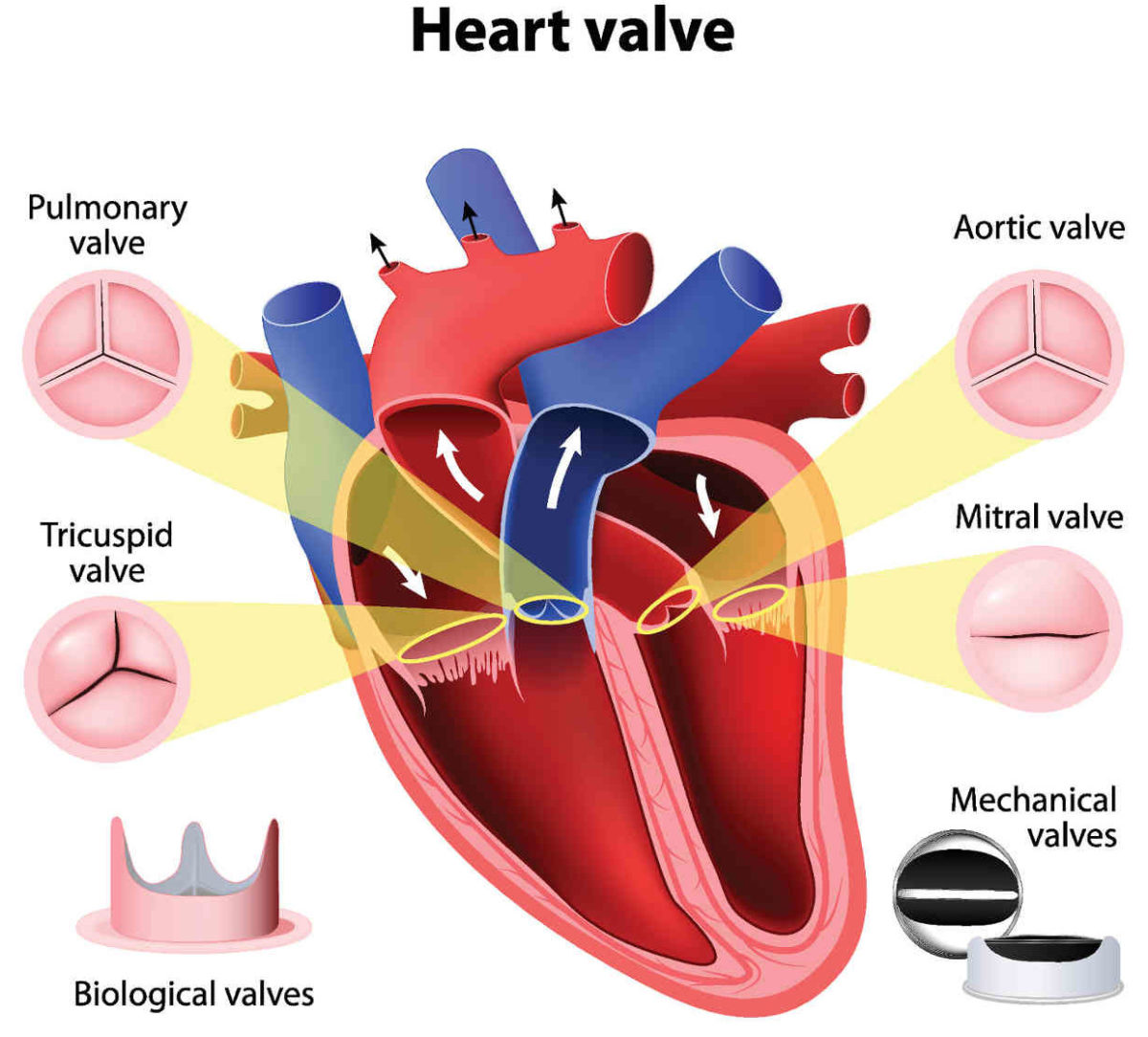
What is the success rate of aortic valve replacement surgery? This question is often asked by patients facing this procedure. The answer depends on a variety of factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the severity of their aortic valve disease.
In general, the success rate of aortic valve replacement surgery is high. According to the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the average survival rate at one year after surgery is 95%. However, this number can vary depending on the factors mentioned above.
Success Rate of Aortic Valve Replacement Surgery: What Is The Success Rate Of Aortic Valve Replacement Surgery
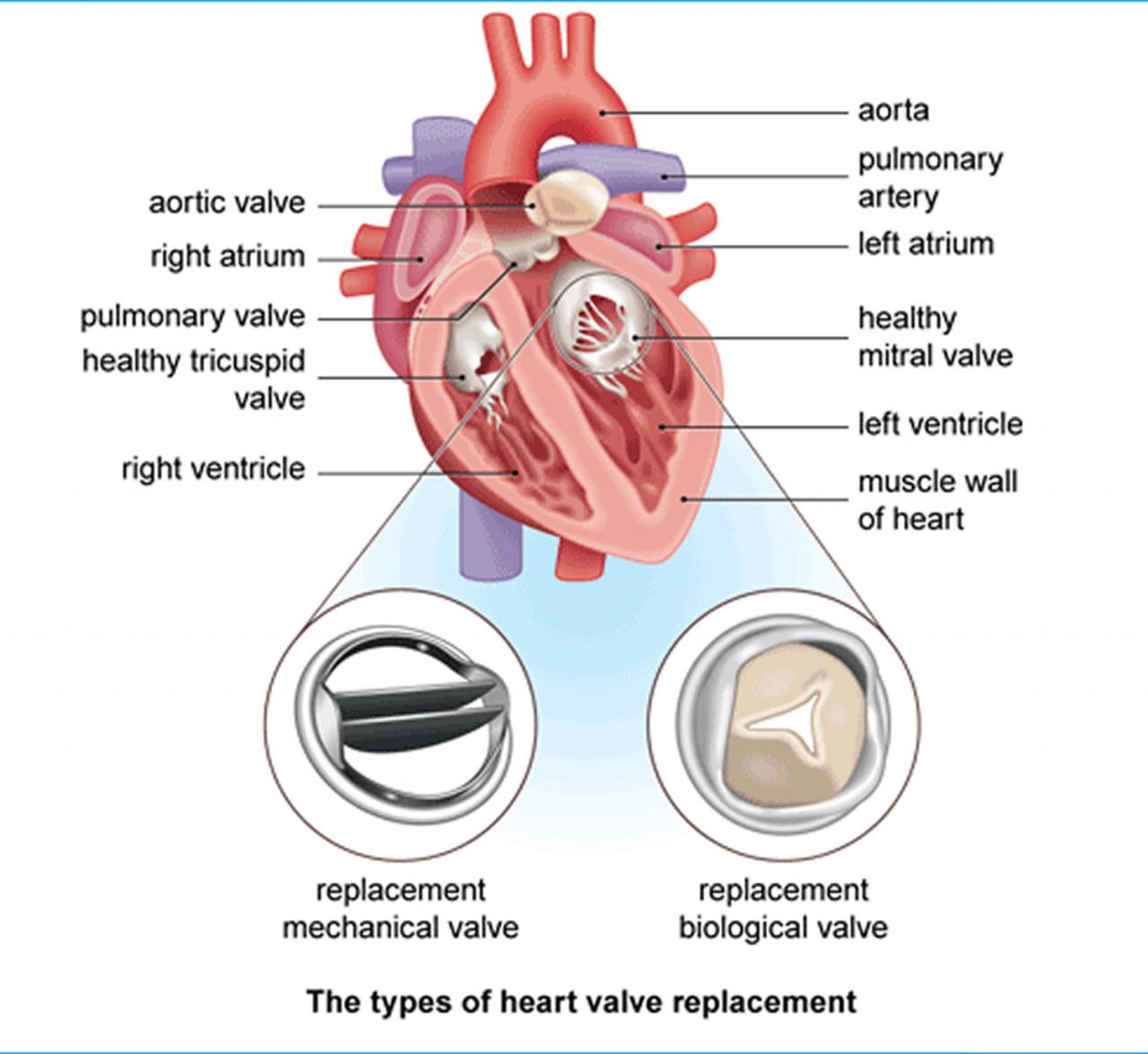
Aortic valve replacement (AVR) surgery is a procedure to replace a damaged or diseased aortic valve with a new valve. The success rate of AVR surgery varies depending on several factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the type of surgery performed.
The overall success rate of AVR surgery is around 90-95%. This means that most patients who undergo AVR surgery experience a significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
Preoperative Factors
Several preoperative factors can affect the success rate of AVR surgery, including:
- Age: The success rate of AVR surgery is generally lower in older patients.
- Overall health: Patients with other medical conditions, such as heart failure or kidney disease, have a higher risk of complications during and after AVR surgery.
- Type of aortic valve disease: The success rate of AVR surgery is higher in patients with aortic stenosis than in patients with aortic regurgitation.
| Preoperative Factor | Success Rate |
|---|---|
| Age < 65 years | 95% |
| Age 65-75 years | 90% |
| Age > 75 years | 85% |
| No other medical conditions | 95% |
| Heart failure | 85% |
| Kidney disease | 80% |
| Aortic stenosis | 95% |
| Aortic regurgitation | 90% |
Surgical Techniques, What is the success rate of aortic valve replacement surgery
There are two main surgical techniques used for AVR surgery: open-heart surgery and transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Open-heart surgeryis the traditional method of AVR surgery. It involves opening the chest and stopping the heart so that the surgeon can replace the aortic valve. Open-heart surgery is a major surgery, but it is the most effective method of AVR surgery.
TAVRis a newer, less invasive method of AVR surgery. It involves inserting a new aortic valve through a small incision in the leg. TAVR is a less risky surgery than open-heart surgery, but it is not as effective in all cases.
The success rate of aortic valve replacement surgery is typically high, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in their symptoms. This procedure is often recommended for individuals with severe aortic valve stenosis, a condition that can lead to heart failure if left untreated.
In related news, jean-philippe mateta has been in excellent form for Crystal Palace this season, scoring several crucial goals. Returning to the topic of aortic valve replacement surgery, the success rate of this procedure is influenced by various factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the severity of their condition.
| Surgical Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Open-heart surgery | More effective | Major surgery |
| TAVR | Less invasive | Not as effective in all cases |
The decision of which surgical technique to use is made on a case-by-case basis. The surgeon will consider the patient’s age, overall health, and the type of aortic valve disease when making this decision.

Final Conclusion
Overall, the success rate of aortic valve replacement surgery is high. However, it is important to remember that this is a major surgery, and there are always risks involved. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of surgery with their doctor before making a decision.