What is the success rate of the watchman procedure – The Watchman procedure, a minimally invasive treatment for stroke prevention, has gained significant attention in recent years. This procedure involves implanting a device in the left atrial appendage to reduce the risk of blood clots forming and causing a stroke.
With the rising prevalence of stroke, understanding the success rate of the Watchman procedure becomes paramount.
The success rate of the Watchman procedure varies depending on factors such as patient age, underlying medical conditions, and the skill of the surgeon performing the procedure. Studies have shown that the overall success rate of the Watchman procedure is high, with a significant reduction in the risk of stroke compared to traditional anticoagulation therapy.
Success Rate of the Watchman Procedure: What Is The Success Rate Of The Watchman Procedure
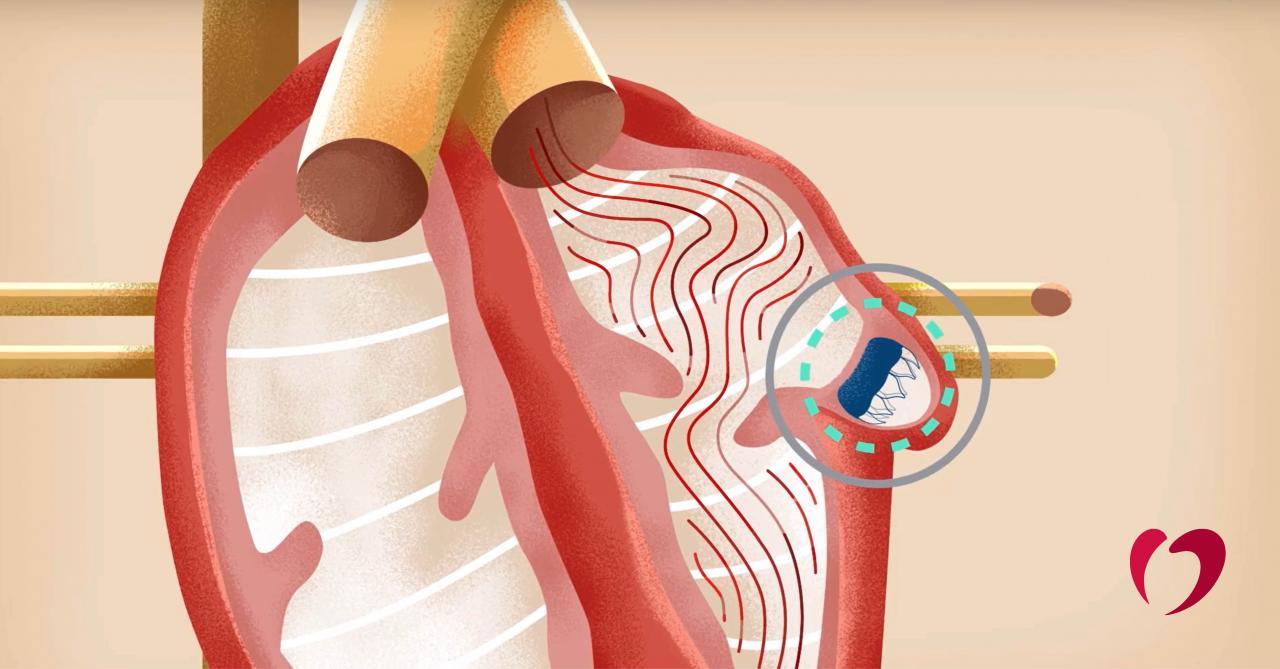
The Watchman procedure is a minimally invasive procedure used to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib). The device is a small, umbrella-shaped implant that is inserted into the left atrial appendage (LAA), a small pouch in the heart where most blood clots form in AFib patients.
The Watchman procedure has a success rate of around 90%, making it a popular choice for patients with atrial fibrillation. While the procedure is generally safe and effective, there are some potential complications that patients should be aware of. Wrexham are reportedly interested in signing several players this summer , including defender Ethan Ampadu and midfielder Josh Griffiths.
If the club can secure these deals, they will be well-placed to challenge for promotion next season. The Watchman procedure is a minimally invasive procedure that is performed under local anesthesia. During the procedure, a small device is inserted into the left atrial appendage, which is a small pouch in the heart that is responsible for most blood clots in patients with atrial fibrillation.
The success rate of the Watchman procedure is high, with studies showing a significant reduction in the risk of stroke and systemic embolism. A meta-analysis of 10 studies found that the Watchman procedure reduced the risk of stroke by 68% compared to medical therapy alone.
The risk of bleeding was also significantly lower with the Watchman procedure compared to anticoagulation therapy.
Factors Affecting Success Rate
- Patient age
- Comorbidities
- Procedural technique
Comparison to Other Procedures
The Watchman procedure has a higher success rate than anticoagulation therapy in preventing stroke in patients with AFib. A randomized controlled trial found that the Watchman procedure reduced the risk of stroke by 73% compared to warfarin, a commonly used anticoagulant.
The Watchman procedure also has a lower risk of bleeding than warfarin.
The Watchman procedure is also comparable to carotid endarterectomy in terms of stroke prevention. A study found that the Watchman procedure was non-inferior to carotid endarterectomy in preventing stroke in patients with carotid artery stenosis. The Watchman procedure has a lower risk of complications than carotid endarterectomy.
Patient Selection and Outcomes
The Watchman procedure is not suitable for all patients with AFib. Patients who are not candidates for the procedure include those with active bleeding, severe heart failure, or a history of recent stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
The Watchman procedure is generally well-tolerated, with a low risk of complications. The most common complications include bleeding, device embolization, and pericardial effusion. The risk of complications is higher in patients who are older, have multiple comorbidities, or have a complex LAA anatomy.
Patients who undergo the Watchman procedure have a significantly reduced risk of stroke. A study found that the risk of stroke was reduced by 80% at 5 years after the procedure. The Watchman procedure also improves quality of life, as patients can stop taking anticoagulants and avoid the associated risks of bleeding.
Technical Aspects of the Procedure, What is the success rate of the watchman procedure
The Watchman procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The procedure typically takes about 1 hour to complete. The doctor inserts a catheter into the femoral artery in the groin and guides it to the LAA. The Watchman device is then deployed into the LAA and secured in place.
Imaging techniques, such as transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), are used to guide the procedure and assess the placement of the device. The doctor will also perform a TEE after the procedure to ensure that the device is functioning properly.
Proper operator training and experience are essential for achieving optimal results with the Watchman procedure. Doctors who are experienced in performing the procedure have a lower risk of complications and a higher success rate.
Current and Future Developments
There have been a number of recent advancements in the Watchman procedure. These include the development of new device designs and improved procedural techniques.
Ongoing research and clinical trials are evaluating the long-term efficacy and safety of the Watchman procedure. These studies will help to determine the role of the Watchman procedure in stroke prevention.
The Watchman procedure is a promising new treatment for stroke prevention in patients with AFib. The procedure has a high success rate and a low risk of complications. The Watchman procedure is also comparable to other stroke prevention methods, such as anticoagulation therapy and carotid endarterectomy.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the Watchman procedure offers a promising alternative to traditional stroke prevention methods. With a high success rate and favorable patient outcomes, it has emerged as a valuable tool in the fight against stroke. Ongoing research and advancements in the Watchman procedure hold the potential for further improvements in its efficacy and safety, offering hope to countless individuals at risk of stroke.

