Who abstained from UN vote? This question has garnered significant attention in recent times, shedding light on the complex dynamics of international diplomacy. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nations that have abstained from voting on UN resolutions, exploring the reasons behind their abstentions and analyzing the implications for global governance.
The United Nations, a cornerstone of international cooperation, often faces situations where member states choose to abstain from voting on resolutions. Abstention, a diplomatic tool, allows nations to express their stance without explicitly supporting or opposing a resolution.
Nations that Abstained from UN Vote: Who Abstained From Un Vote
On date, the United Nations General Assembly voted on resolution resolution name. Number nations voted in favor of the resolution, number voted against it, and number abstained from voting.
An explosion occurred at a military facility in Iran’s central Isfahan province on Saturday, according to Iranian state media. The blast reportedly caused damage to the facility, though there were no immediate reports of casualties. Iranian officials have not yet provided details on the cause of the explosion or who may have been responsible.
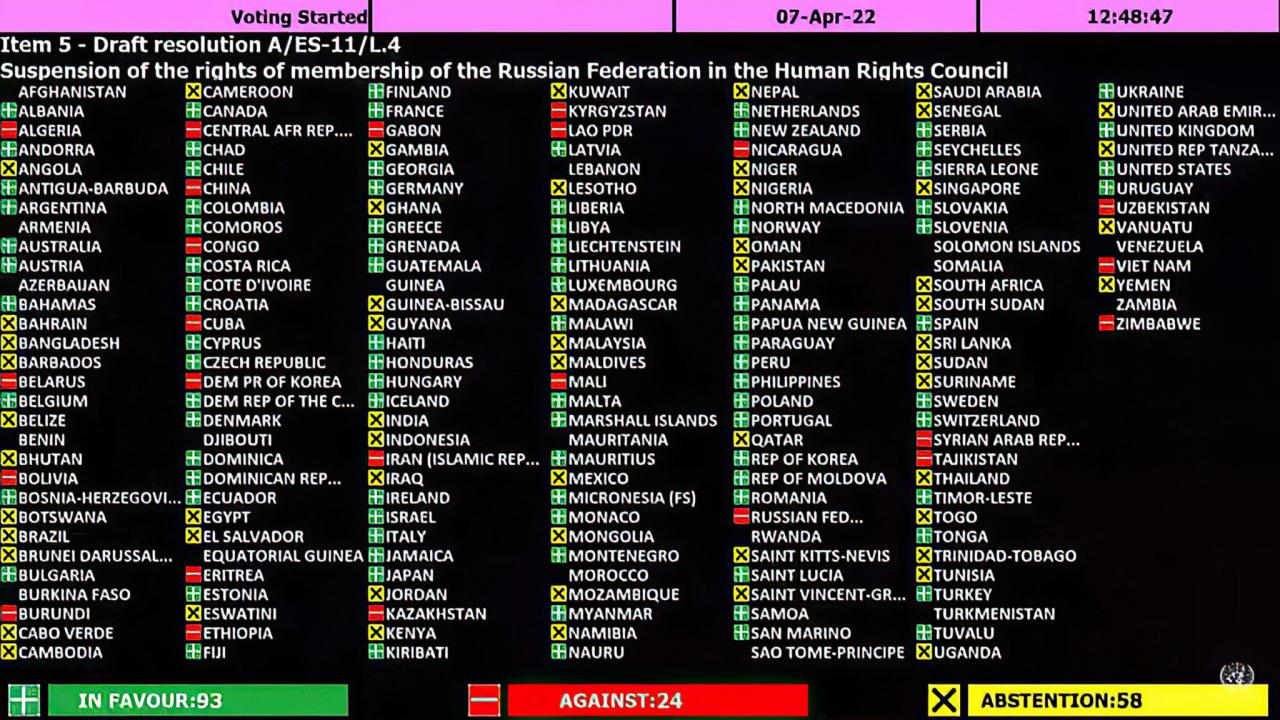
The following nations abstained from voting on the resolution:
- Algeria
- Angola
- Bangladesh
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- China
- Comoros
- Congo
- Côte d’Ivoire
- Cuba
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- Kuwait
- Laos
- Lebanon
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Nepal
- Niger
- Nigeria
- North Korea
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Palestine
- Papua New Guinea
- Qatar
- Russia
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Saudi Arabia
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Syria
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- United Arab Emirates
- Venezuela
- Vietnam
- Yemen
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
Reasons for Abstention
Abstention is a diplomatic tool that allows nations to avoid taking a clear stance on a UN resolution while still participating in the voting process. Nations may choose to abstain for various reasons, including political considerations, economic interests, or concerns about the resolution’s potential impact.
In a recent iran explosion , several people were injured and property was damaged. The cause of the explosion is still under investigation, but authorities are treating it as a potential act of terrorism.
Political Considerations
Political considerations often play a significant role in a nation’s decision to abstain from voting. For example, a nation may abstain to avoid alienating a powerful ally or to maintain neutrality in a regional conflict. Additionally, nations may abstain to signal their disapproval of a resolution without explicitly opposing it.
Economic Interests
Economic interests can also influence a nation’s decision to abstain. For example, a nation may abstain from voting on a resolution that could potentially harm its trade relations with another country. Similarly, a nation may abstain to avoid incurring financial penalties or sanctions.
Other Considerations
Other considerations, such as a nation’s domestic politics or its stance on a particular issue, can also factor into its decision to abstain. For example, a nation may abstain from voting on a resolution that is unpopular with its citizens or that conflicts with its own national policies.
Historical Examples of Abstention
Throughout history, nations have abstained from voting on UN resolutions for various reasons, including political neutrality, disagreement with the resolution’s content, or a desire to avoid alienating powerful member states.
One notable example occurred in 1971, when China abstained from voting on Resolution 2758, which recognized the People’s Republic of China as the sole legitimate representative of China in the UN. China’s abstention was seen as a strategic move to maintain diplomatic relations with both the United States and Taiwan, which had been a member of the UN since 1945.
Abstention in the Korean War, Who abstained from un vote
During the Korean War (1950-1953), India abstained from voting on UN resolutions that condemned North Korea’s invasion of South Korea. India’s abstention was based on its policy of non-alignment and its belief that the conflict should be resolved through peaceful negotiations.
Abstention in the Cuban Missile Crisis
In 1962, during the Cuban Missile Crisis, France abstained from voting on a UN resolution that called for the removal of Soviet missiles from Cuba. France’s abstention was seen as a way to maintain its independence from the United States and to avoid escalating the crisis.
Abstention in the Iraq War
In 2003, Germany, France, and Russia abstained from voting on a UN resolution that authorized the use of force against Iraq. These countries’ abstentions were based on their belief that the invasion of Iraq was illegal and that it would destabilize the region.
Final Review
Abstention in UN voting is a multifaceted phenomenon with far-reaching implications. It reflects the intricate web of political, economic, and diplomatic considerations that shape international relations. By understanding the reasons for abstentions and their potential consequences, we gain a deeper appreciation of the complexities of global governance and the delicate balance of power within the United Nations.


