What are the differences between primary succession and secondary succession? Primary succession refers to the establishment of an ecosystem in an area that has never been vegetated before, while secondary succession occurs in an area that has been previously vegetated but has been disturbed or cleared.
Both primary and secondary succession involve the gradual development of an ecosystem, but they differ in their starting points and the rate at which they progress.
What Are the Differences Between Primary and Secondary Succession?

Ecological succession refers to the gradual changes in species composition and community structure over time. Primary succession occurs on previously barren or disturbed areas, while secondary succession takes place in areas that have been previously vegetated but disturbed.
Key Differences in Initiation and Establishment
| Factor | Primary Succession | Secondary Succession |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation | No pre-existing soil or vegetation | Soil and vegetation present, but disturbed |
| Establishment | Pioneer species (lichens, mosses) colonize bare rock or soil | Early successional species (grasses, shrubs) establish quickly |
Soil and Nutrient Availability
In primary succession, soil is initially absent or poorly developed. Nutrients are scarce, and organic matter accumulates slowly. In secondary succession, soil is already present and contains nutrients from the previous vegetation. Nutrient availability is generally higher than in primary succession.
Species Composition and Diversity
Species composition changes over time in both primary and secondary succession. In primary succession, pioneer species are initially dominant, followed by early successional species, and eventually late successional species. In secondary succession, early successional species are initially dominant, but they are gradually replaced by late successional species.
Primary succession occurs on new or exposed surfaces, while secondary succession takes place on sites where vegetation has been cleared or disturbed. Both processes involve the gradual reestablishment of plant communities, but they differ in their starting points and the rate at which they progress.
For more information on the timing of tomorrow’s Supreme Court hearing, please visit this link . The differences between primary and secondary succession are significant and have implications for ecosystem management and restoration.
Time Scales and Recovery Rates
| Factor | Primary Succession | Secondary Succession |
|---|---|---|
| Time Scale | Hundreds to thousands of years | Decades to centuries |
| Recovery Rate | Slow, limited by nutrient availability and harsh conditions | Faster, due to presence of soil and seed bank |
Examples and Case Studies, What are the differences between primary succession and secondary succession
Examples of primary succession include the colonization of lava flows and the development of soil on glacial moraines. Examples of secondary succession include the regrowth of vegetation after a forest fire or the abandonment of agricultural land.
Case studies have shown that primary succession can take centuries or even millennia to reach a stable ecosystem, while secondary succession can occur much more rapidly. The recovery rate of an ecosystem undergoing succession depends on factors such as the severity of the disturbance, the availability of resources, and the climate.
Final Wrap-Up: What Are The Differences Between Primary Succession And Secondary Succession
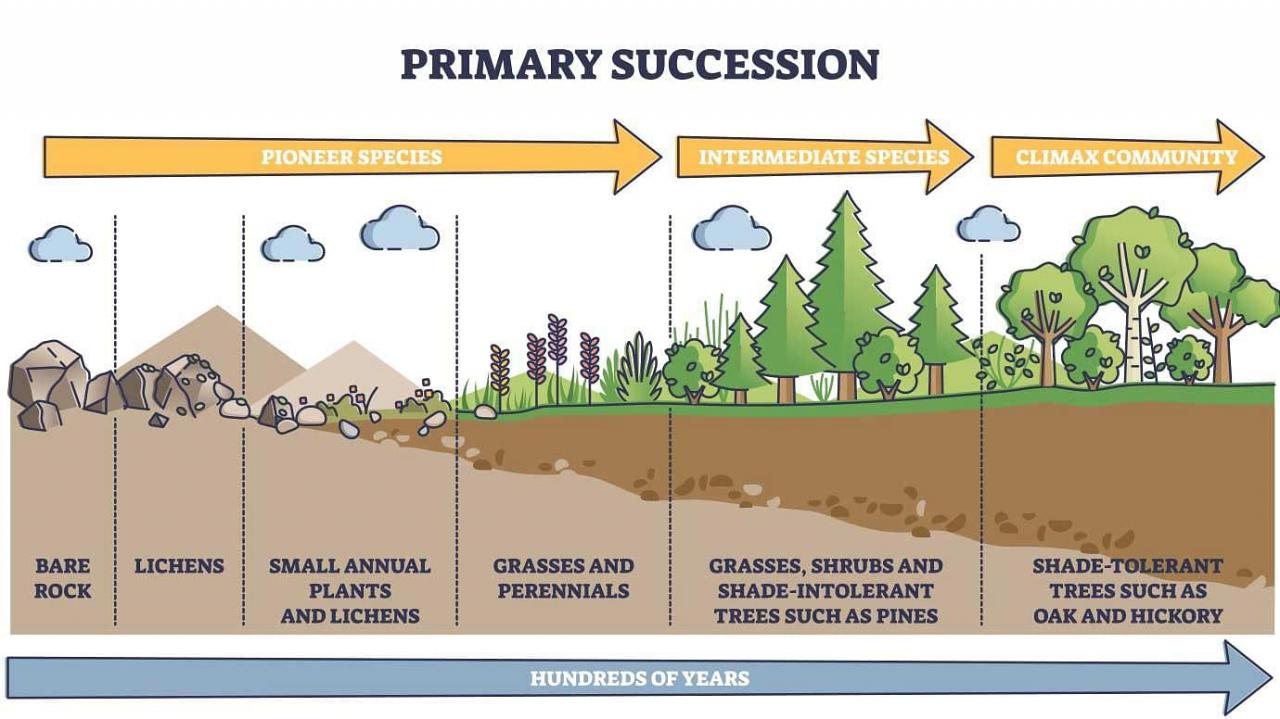
In summary, primary and secondary succession are two distinct processes that contribute to the development of ecosystems. Understanding the differences between these two types of succession is essential for comprehending the dynamics of ecological communities and the resilience of ecosystems in the face of disturbance.


